
Light-vented bulbul (Pycnonotus sinensis), one of the species of interest in the Ryūkyū archipelago.
Biogeography is often more complicated than the species-area relationship as discussed in a recent Journal of Animal Ecology paper testing multiple extensions of island biogeography theory. Sam Ross, lead author of the study, describes how this work fits into the long history of biogeography research.
The species-area relationship is considered one of the only ‘rules’ in ecology. We have observed more species on larger ‘islands’ (whether true islands or simply some habitat patch of interest) in studies of different plants and animals all around the world. When MacArthur and Wilson (1967) proposed this pattern and the pioneering biogeographical principles which underpin it, they acknowledged that a piece of the puzzle was missing: species identity.
Biogeographers have since recognised that species aren’t randomly distributed across the globe. We now believe there to be ecological factors which predict where species occur. For example, predators can only live in habitats where their prey are sufficiently abundant, otherwise they’ll starve. This led Dominique Gravel and colleagues to predict that larger islands should have more complex food webs, since smaller islands support fewer prey species and so can in turn support fewer, if any, predators (Gravel et al. 2011). They then proposed that predators should be more influenced by island size than their prey, producing steeper species-area relationships for higher trophic levels. They called this idea the ‘trophic theory of island biogeography.’
We tested this empirically using checklists of bird sightings across the Ryūkyū archipelago running from southern mainland Japan to Taiwan. We separated birds by their trophic groups and found that contrary to the trophic theory of island biogeography, our predatory birds didn’t really differ in the slope of their species-area relationship from our herbivorous birds. This wasn’t really what we expected to find but the trophic theory hasn’t yet been tested across a range of different study systems, so our test helps us to understand whether communities may be structured by trophic level or not.
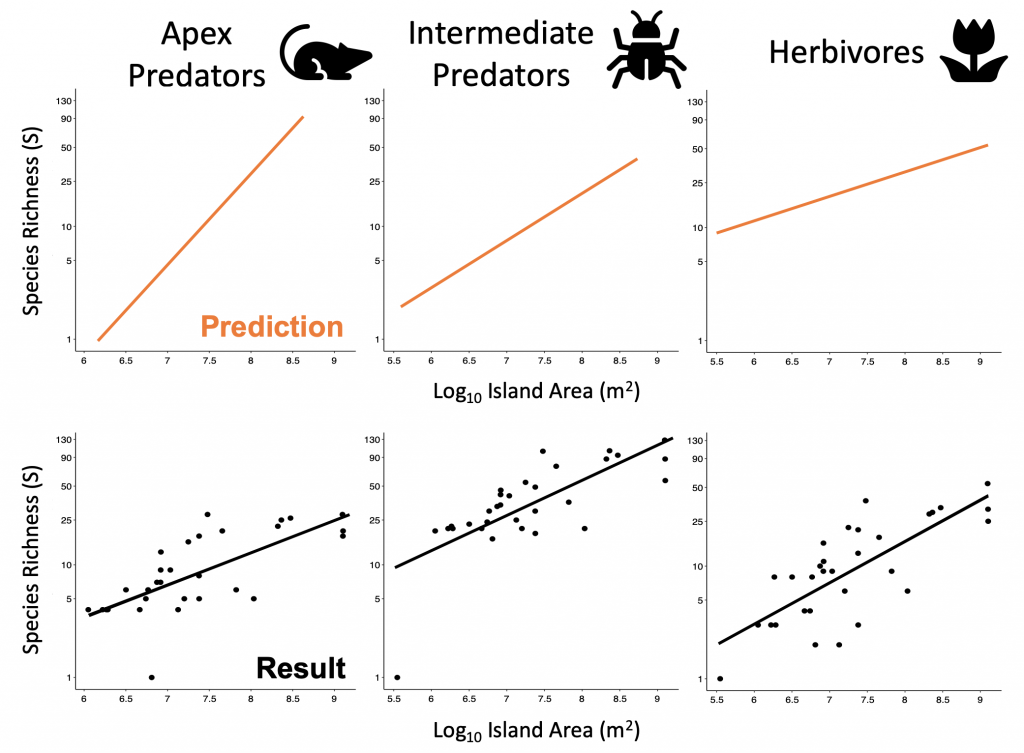
Expectation versus reality of our test of the trophic theory of island biogeography with the birds of the Ryūkyūs.
Another way species’ identities might structure communities is based on the idea of environmental filtering. These filters are thought to be strongest on small islands, where there is little opportunity to just scrape by. Small islands are harsh; there are many ways populations can go extinct on small islands, but particularly life on these islands is strongly affected by environmental conditions. This means that only species particularly suited to the environment are likely to survive and thrive on small islands. By expanding on the work of Claire Jacquet and colleagues (Jacquet et al. 2017), we could then predict that small islands would have species which are similar to each other and are all adapted to the local environment, whereas larger islands are more likely to contain random species from the regional pool of all species which could possibly live there.
Another longstanding idea predicts the opposite pattern. Because smaller islands have fewer resources, species must compete for those finite resources to survive. This means that on small islands, we might expect species to be widely different from each other to minimise competition for food and space. If there’s only one small grasshopper population on the island for example, it seems more likely that we’ll find five species of birds that all eat different things than five that are competing for the chance to eat this one grasshopper. So, we might expect that competition results in distinctive species on smaller islands and that as competitive pressure relaxes on larger islands, these islands again are more likely to contain a random assortment of species.

Blue Rock Thrush (Monticola solitarius) pictured at Cape Zanpa, Okinawa—the edge of the island.
We tested whether either of these two processes structured the bird communities of the Ryūkyūs by calculating the functional and phylogenetic diversity of birds on each island using two global databases. We used the global phylogeny of birds and a database of functional traits to measure the observed functional and phylogenetic diversity of birds on each of our study islands. We also tested whether this observed diversity was higher or lower than expected by random chance by shuffling the names of species on the phylogeny and functional trait matrix. Together, this meant we could test whether diversity was lower than expected by random on small islands and increasing to a random sample of the regional pool (trait-based assembly), or whether competitive assembly occurred, where diversity was higher than expected on small islands and closer to random on larger islands.
We found no clear overall pattern of either trait-based or competitive assembly of bird communities in the Ryūkyūs, but we did find some differences among our trophic groups in whether communities were structured randomly or not. The insectivorous intermediate predators showed patterns of trait-based community assembly since their phylogenetic and functional diversity was lower than expected on small islands and increased to random on larger islands.
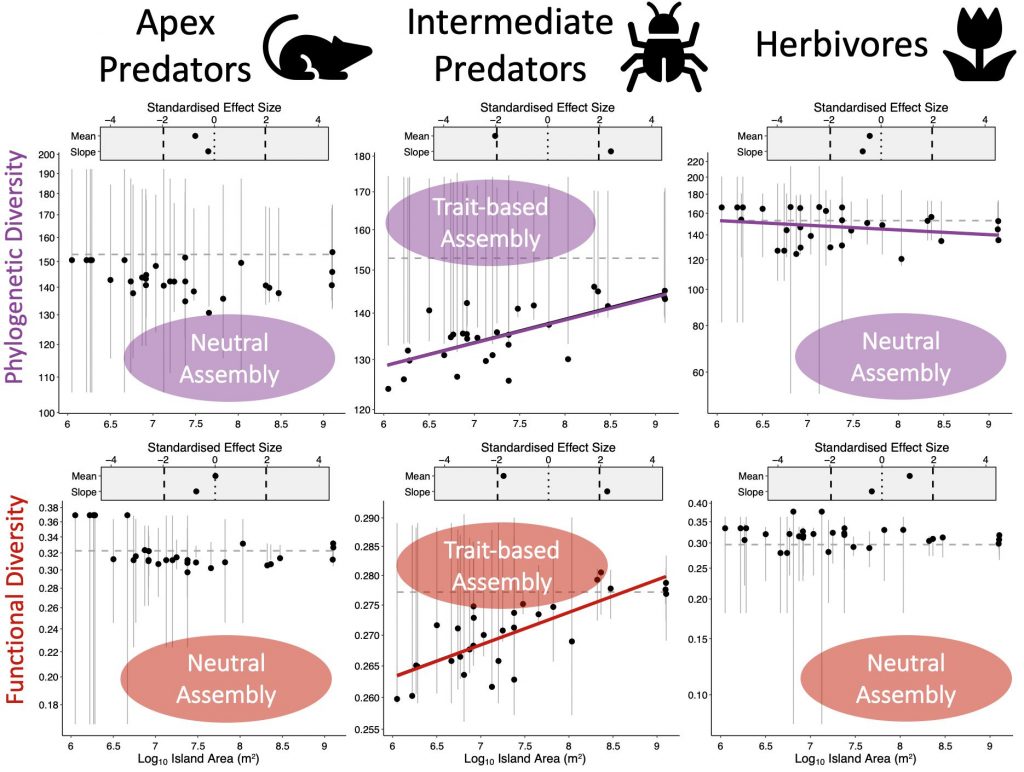
Community assembly processes across our trophic groups of birds. We found no clear patterns for apex predators or herbivores, but intermediate predators followed the predictions of trait scaling by Jacquet et al. (2017).
Overall, we tested multiple extensions to the theory of island biogeography which have been rarely tested, and certainly not extensively across a range of study locations and focal species. In the subtropical Ryūkyū archipelago, we found that bird communities did not clearly conform to the theories laid out by recent extensions to island biogeography theory, but that some held true. For now, we encourage others to continue testing these hypotheses in a variety of study systems to see whether our subtropical bird communities show the same biogeographic patterns as animal communities around the world.
This post is written by: Sam Ross, a PhD student at Trinity College Dublin studying ecological responses to global change and a visiting research student at the Arilab.
More Info:
Ross, S. R. P-J., Friedman, N. R., Janicki, J., & Economo, E. P. (2019). A test of trophic and functional island biogeography theory with the avifauna of a continental archipelago. Journal of Animal Ecology. DOI: 10.1111/1365-2656.13029
You can read the full paper here.
