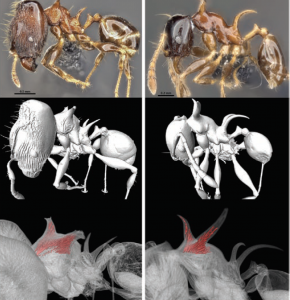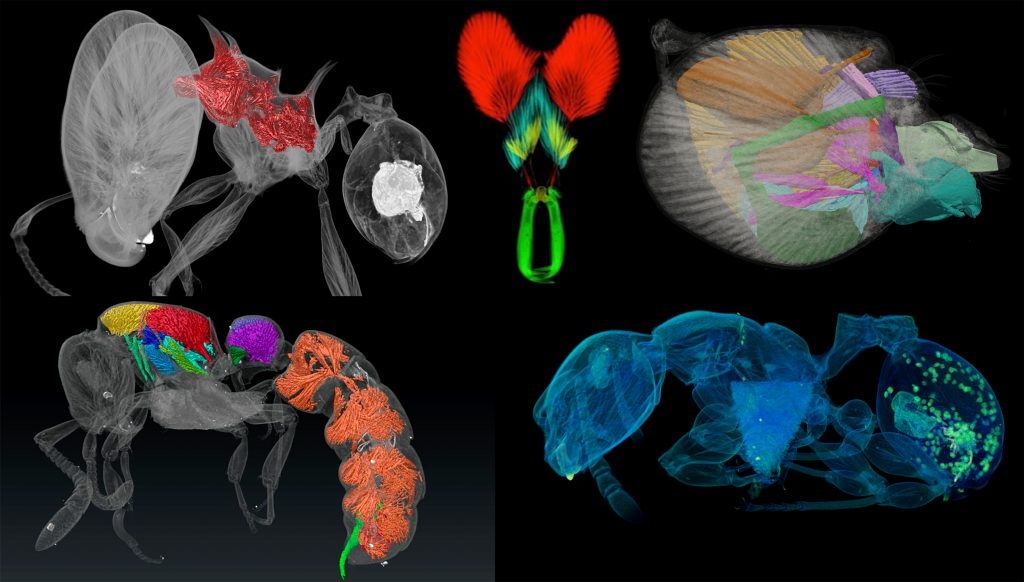
Last week our lab hosted an OIST Mini Symposium titled “Advances in imaging, quantifying, and understanding the evolution of ant phenotypes” organized by Evan Economo and Francisco Hita Garcia. The aim of the symposium was to gather a small but selected group of leading researchers interested in the evolution of ant phenotypes with a strong focus on the use of x-ray microtomography (micro-CT). Our list of speakers covered experts in the fields of molecular and morphological systematics, anatomy, functional morphology, comparative morphology, adaptive trait evolution, reproductive biology, linear and geometric morphometrics, and paleontology. All invitees gave outstanding talks and presented published or ongoing research in great detail and with beautiful 2D or 3D illustrations and/or videos.
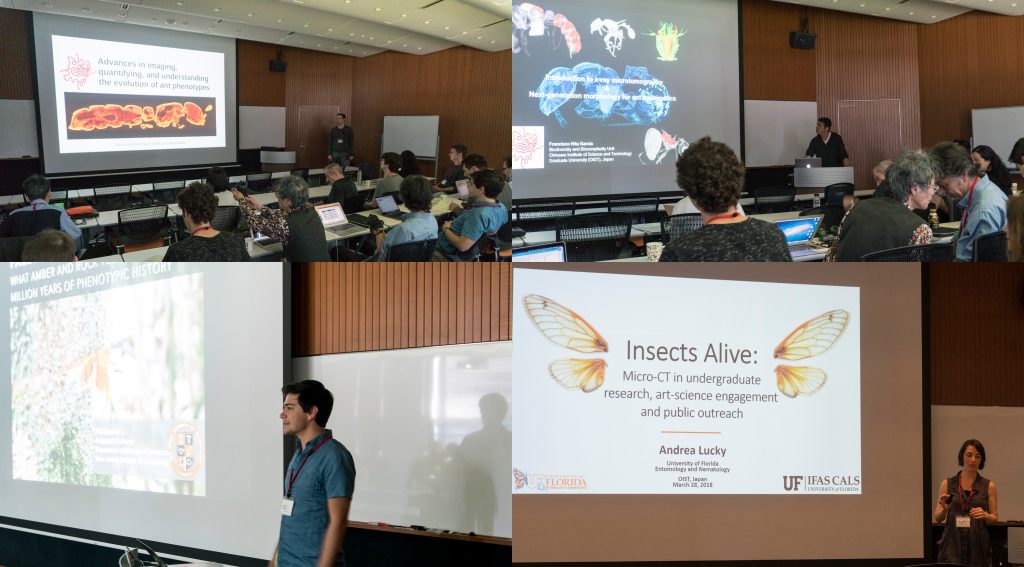

Some talks provided conceptual and technical backgrounds and perspectives of how to use micro-CT for ant morphology, how to better integrate next-generation phenomics into systematics, palaeontology, and evolutionary biology, and how to use micro-CT data and downstream 3D applications for education and public outreach.

A strong focus of the symposium was the use of micro-CT for ant functional morphology, biomechanics, and the evolution of complex phenotypes. Some guests also showed recent advances in histology-based anatomy and reproductive biology, and shared ideas of how to combine traditional histology with modern 3D imaging technologies, such as micro-CT.

We also had a session focusing on the use of 2D linear and 3D geometric morphometrics and their application for ant phylogenetics, taxonomy, trait evolution, and more generally how to use large 3D phenotypical datasets to answer questions in evolutionary biology.

One afternoon was completely devoted to practical demonstrations of how to use 3D data. Our lab shared how we scan data post-processing, 3D virtual reconstructions, 3D animations, virtual/augmented reality, 3D printing. It was useful for sharing knowledge of methodology, and stimulating ideas for future directions and applications.

The three-day symposium provided ample opportunities for socializing and chatting about on-going and potential collaborations, discussions about methods and research results, as well as brainstorming about future directions for the field. At the same time our invitees got the chance to enjoy Japanese and Okinawan culture and cuisine and show off their Karaoke skills.
Invited speakers:
Phil Barden (New Jersey Institute of Technology)
Johan Billen (KU Leuven)
Benjamin Blanchard (U. Chicago and Field Museum)
Ayako Gotoh (Konan U.)
Yoshiaki Hashimoto (U. Hyogo, Museum of Nature and Human Activities, Hyogo)
Fuminori Ito (Kagawa U.)
Roberto Keller (Museu Nacional de História Natural e da Ciência)
Andrea Lucky (U. Florida)
Christian Peeters (U. Pierre et Marie Curie)
Shauna Price (Field Museum)
Andrew Suarez (U. Illinois)
Internal speakers:
Evan P. Economo
Georg Fischer
Nick Friedman
Francisco Hita Garcia
Adam Khalife (U. Pierre et Marie Curie and OIST)